Why is My PC Overheating? 12 Causes, Fixes & Thermal Paste Guide,Fixing Thermal Throttling.
Is your laptop screaming like a jet engine? Does your PC slow down the moment you start a game? If so, you are experiencing Thermal Throttling.Fixing Thermal Throttling.
Check your PC Stress Test

PCs have had heat issues since day one, and even with the newest tech, we still haven't fully fixed it.
Back in the day, when we used our old PCs for gaming, our biggest headache was the computer slowing down. As kids, we had no idea why it happened, but we noticed that the moment we pushed the machine a little, the fan would start roaring like an airplane engine. I still vividly remember 2002—playing games like IGI and GTA Vice City on a Pentium 4. After just a few minutes, alongside the game sounds, you’d hear a terrifying mechanical noise coming not from the speakers, but from the CPU tower itself. I can still hear that sound in my head!
Back then, “tech experts” told us that Pentium 4 processors just ran hot, and that’s why they lagged. I remember frequently taking the side cover off the CPU and pointing a big pedestal fan at it just so I could enjoy my games for a bit longer. Even then, it didn’t help much.


Technology has come a long way since then, and modern hardware is much more efficient. However, gamers today still struggle with overheating and loud fans. The core problem hasn’t changed much since our childhood; as hardware got faster, software and games became much heavier, keeping the cycle of heat alive. In today’s article, I’ll guide you on how to properly maintain your laptop or PC, identify why it’s overheating, and how to fix these issues. Read until the end—I’m sure this will help solve your problems.
10 Reasons Why Our PC Overheats

Too Many Programs Running
Dust Accumulation
Outdated Hardware
Obstruction in Airflow
Virus or Malware
Background Processes
Browser Overload
Outdated OS or Software
Fan Malfunction or Not Working
Thermal Paste Drying Out
1.Too Many Programs are Running
Sometimes the hardware is fine, but the software is too demanding. If you try to run a heavy program on a low-end PC, the CPU stays at 100% usage. This constant stress generates massive heat. Keep an eye on your Task Manager and close programs you aren’t using.


2.Dust Accumulation:
Remember, just like everything else needs cleaning and maintenance, computer hardware also needs regular cleaning. If a computer isn’t cleaned for a long time and dust accumulates on the fan and other components, the computer’s performance can suffer. A major heating issue in laptops or desktops often arises due to dust buildup inside the hardware and the fan. This dust prevents the fan from functioning properly, causing the processor and GPU to overheat, thus slowing down the computer. It’s crucial to clean your computer hardware periodically, especially the fans, to allow the GPU and CPU to cool down properly. The more frequently you clean, the better the system will perform. If you can clean the internal parts of your computer yourself, that’s great, but if you’re new to this, it’s better to get professional help. Cleaning your computer can significantly reduce or even completely solve the heating problem, enabling you to enjoy gaming smoothly.
3.Outdated Hardware
Since technology is evolving rapidly, older hardware may not support the latest software. For example, trying to run modern software on an old Pentium IV system could cause the computer to overheat and shut down. In such cases, upgrading the hardware is necessary.

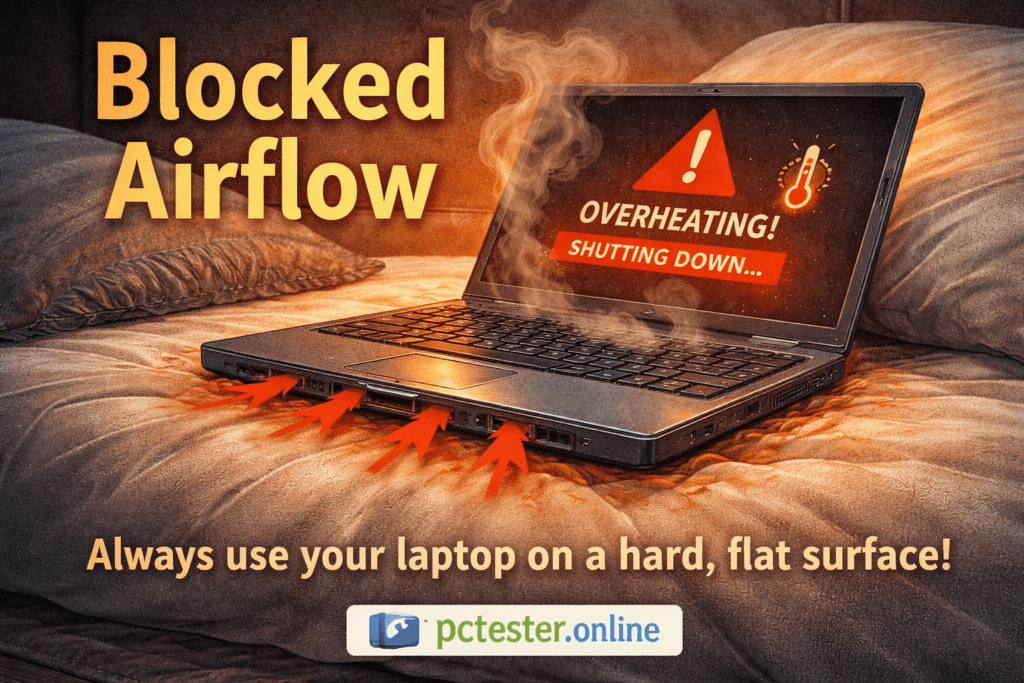
4.Obstruction in Airflow:
The design of a computer system is such that airflow is crucial for cooling the components. However, if you use your laptop on soft surfaces like a bed or blanket, the airflow can be blocked. This results in the hot air getting trapped inside, making the system overheat. To prevent this, always use a laptop on a hard surface or with a cooling pad.
5.Virus or Malware:
Sometimes, your computer’s hardware may be fine, but a virus or malware can overload the processor, causing it to overheat. Use a good antivirus program to protect your system from these threats.


6.Background Processing:
Heavy background programs or applications can cause the computer to overheat. If a computer’s hardware isn’t capable of handling resource-heavy software, it works at full capacity, causing it to overheat and slow down. To prevent this, check your system’s specifications and avoid running multiple resource-heavy applications simultaneously.
7.Browser Overload:
Having too many tabs open in a browser can overload your system. Close unnecessary tabs and keep the number of open applications minimal to reduce load on your computer.


8.Outdated OS or software
Outdated OS or software may not have the latest updates that optimize how the computer uses its hardware resources, such as the CPU, RAM, and GPU. These older programs can demand more resources than necessary, causing the system to work harder than it should, which leads to increased power consumption and higher heat generation.
For example, older versions of an OS may not effectively manage background processes, causing them to run unnecessarily and consuming more processing power, which can overheat the CPU.
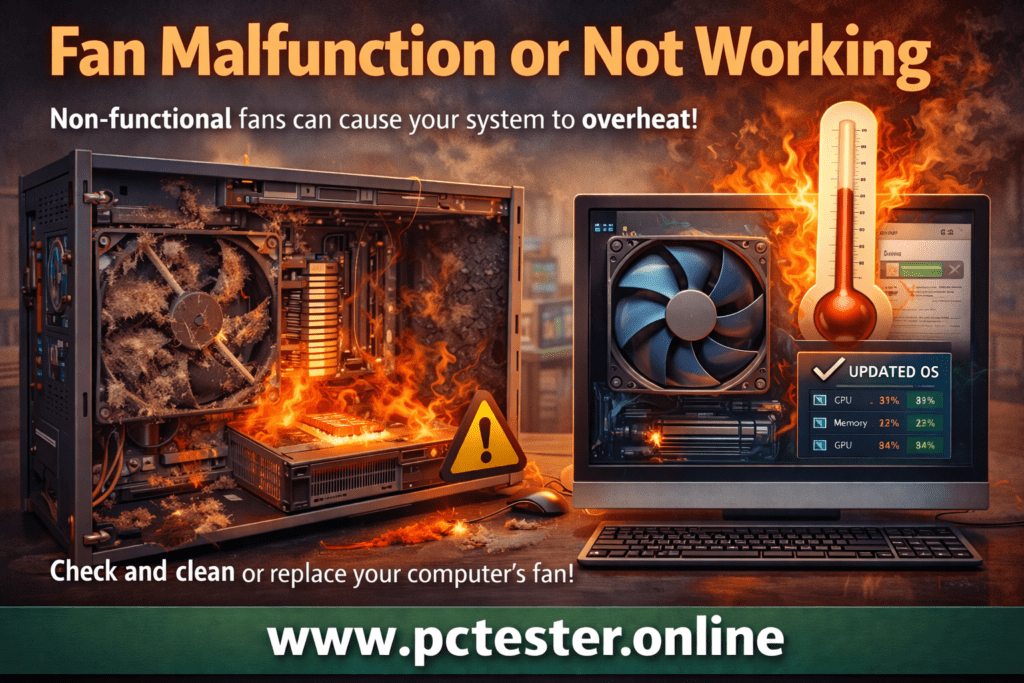
9.Fan Malfunction or Not Working
Sometimes, the fans inside a computer stop working or slow down due to dust and debris buildup. When the fan fails, the heatsink cannot cool the system properly, leading to overheating. This is a common cause of laptop overheating and frequent restarts. If your computer is heating up, the fan should be checked, cleaned, or replaced if necessary.
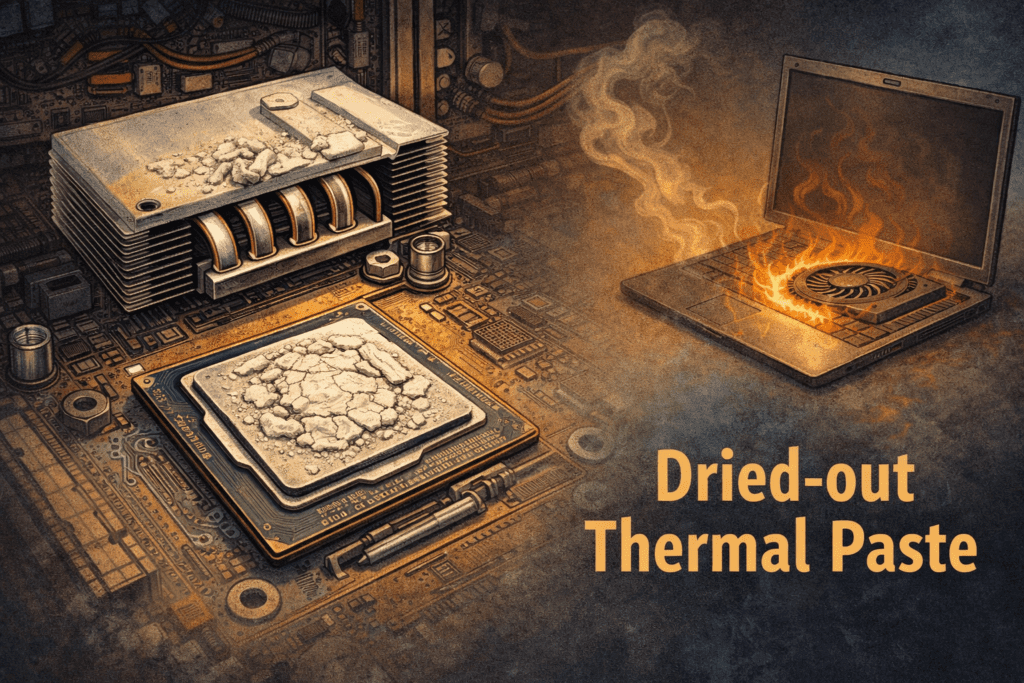

Thermal Paste Drying Out
I remember the first time I opened my PC in my life. When I saw that silver-colored paste under the processor’s heatsink, I was genuinely surprised. At that time, I thought it was some kind of magical cream. Back then, we didn’t realize that this simple-looking paste could decide the life or death of our expensive hardware.
Thermal paste is extremely important. It transfers heat from the CPU and GPU to the heatsink, which is then cooled by the fan’s airflow. This process keeps a laptop or computer cool and prevents overheating.
Over time, especially as a computer gets older, thermal paste dries out and stops working efficiently. When this happens, heat from the CPU or GPU does not transfer properly to the heatsink. As a result, the fan ends up cooling only the heatsink, while the processor or GPU itself remains hot.
When you turn on your laptop or computer, it may start heating up after a short time, and the fan may begin spinning very fast, producing an unusually loud noise. If you are experiencing this issue, it is a clear sign that your computer needs thermal repasting.
If you can easily replace the thermal paste yourself, that’s great. However, this is a very important and delicate task. If you are new to this, it’s better to seek help from a professional computer technician who can properly clean your laptop or computer and apply high-quality thermal paste.
10.Types of Thermal Paste
I remember that when we were younger, we used a “hack” to cool our PCs. When thermal paste dried out, we used to apply toothpaste instead. It worked for a short time because toothpaste contains moisture, but after a few hours, it would dry out and harden like stone. Not only would it stop working, but it could also damage the hardware. At that time, we didn’t fully understand these things.
Now, let’s discuss the types of thermal paste.
There are three main types of thermal paste:
1. Ceramic Thermal Paste
Ceramic thermal paste is usually inexpensive and white in color, often resembling white toothpaste. It is non-conductive, making it safe because it only transfers heat and does not damage computer hardware. While it works well for a short period, it is not very effective for long-term use.
2. Silver (Metal-Based) Thermal Paste
This type contains silver particles that fill the microscopic gaps between the CPU or GPU and the heatsink. It transfers heat efficiently from the processor to the heatsink, where the fan cools it down. This keeps the computer at a stable temperature.
Silver thermal paste is not very expensive and works well for normal computers and laptops. However, it is not ideal for high-performance gaming PCs or systems with powerful graphics cards. If you use a standard computer and do not do heavy gaming, this paste is usually sufficient.
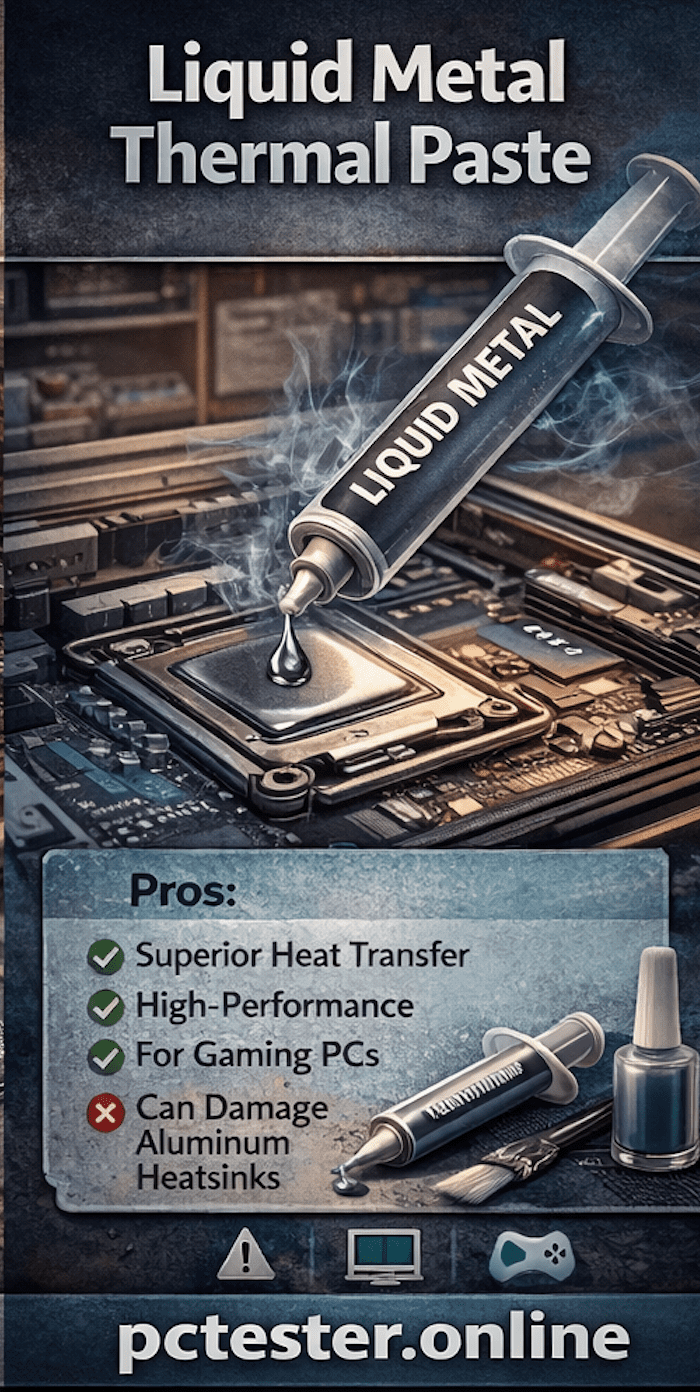
3. Liquid Metal Thermal Paste
Liquid metal thermal paste is used in high-performance systems, especially gaming PCs. While regular thermal paste works like a simple cream, liquid metal behaves like molten metal and has exceptional heat transfer capability.
However, the more powerful it is, the more dangerous it can be. Liquid metal is typically a mixture of metals such as gallium, indium, and tin. One of its key properties is that it remains in liquid form at room temperature.
The biggest difference between regular thermal paste and liquid metal is thermal conductivity, which refers to how fast heat transfers from one component to another.
Regular thermal paste: approximately 5–10 W/mK
Liquid metal thermal paste: approximately 73 W/mK
This means liquid metal transfers heat many times faster than standard thermal paste.
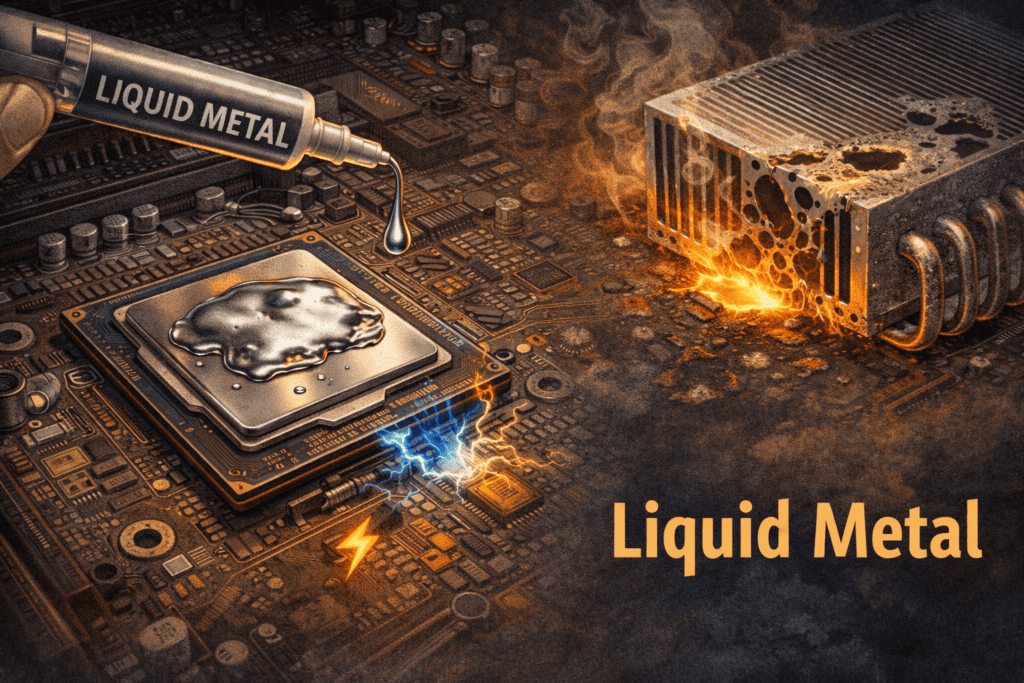
Extreme caution is required when applying liquid metal. Gallium reacts chemically with aluminum, causing a reaction known as gallium embrittlement. If your heatsink is made of aluminum, it can weaken, crack, or even disintegrate like paper. Therefore, liquid metal should only be used with copper or nickel-plated heatsinks.
Another important point is that regular thermal pastes are non-conductive, while liquid metal is highly conductive. Even a tiny drop falling on the small capacitors or components around the processor can short-circuit and permanently damage them. For safety, technicians often use nail polish, electrical tape, or other insulating materials around the CPU before applying liquid metal.
When applying liquid metal, use a special applicator or cotton swab to spread a very thin layer over the processor. A very small amount is enough. Applying too much can cause the liquid metal to leak onto the motherboard and damage other components.



PlayStation 5 and Liquid Metal Thermal Paste
If you’ve ever noticed how quiet the PlayStation 5 is, liquid metal thermal paste is one of the main reasons. Sony uses liquid metal instead of traditional thermal paste in the PS5. To prevent leakage, Sony designed a specially sealed and coated barrier so the liquid metal cannot escape and damage the motherboard.
This is why the PS5 remains cool and operates quietly.
You may remember mercury thermometers from childhood. When they broke, the mercury inside would form small, fast-moving droplets. Liquid metal thermal paste looks and behaves very similarly to mercury.
If you are using liquid metal thermal paste for the first time, it is strongly recommended not to do it yourself. Instead, have the job done by an experienced technician. Even a small mistake can permanently damage your laptop or computer.
How to Prevent a Computer or Laptop from Overheating
By following a few precautionary measures, we can protect our computers and achieve better performance.
1. Keep the Computer Clean
Make sure your computer is clean so that dust and debris do not accumulate inside and the fans remain clear. Over time, fans can become dirty or dry due to continuous use. If your computer’s fan is dirty or making noise, first clean it thoroughly and then apply a lubricant specifically designed for computer fans.
Using proper lubricant helps eliminate fan noise and improves fan speed. Whether you have a new or an old laptop, it is recommended to clean it at least once a year. If you live in a dusty or polluted environment, reduce the cleaning interval and clean it more frequently.
2. Maintain Proper Airflow
Both laptops and desktop computers have dedicated air vents for fresh airflow. If these air passages become blocked, fresh air cannot enter the system, and the heat generated inside has no way to escape. This causes the computer to heat up rapidly.
For this reason, always use your computer on a hard, flat surface or on a laptop cooling pad. Avoid using it on pillows, blankets, or soft surfaces, as they block airflow and increase the risk of overheating.

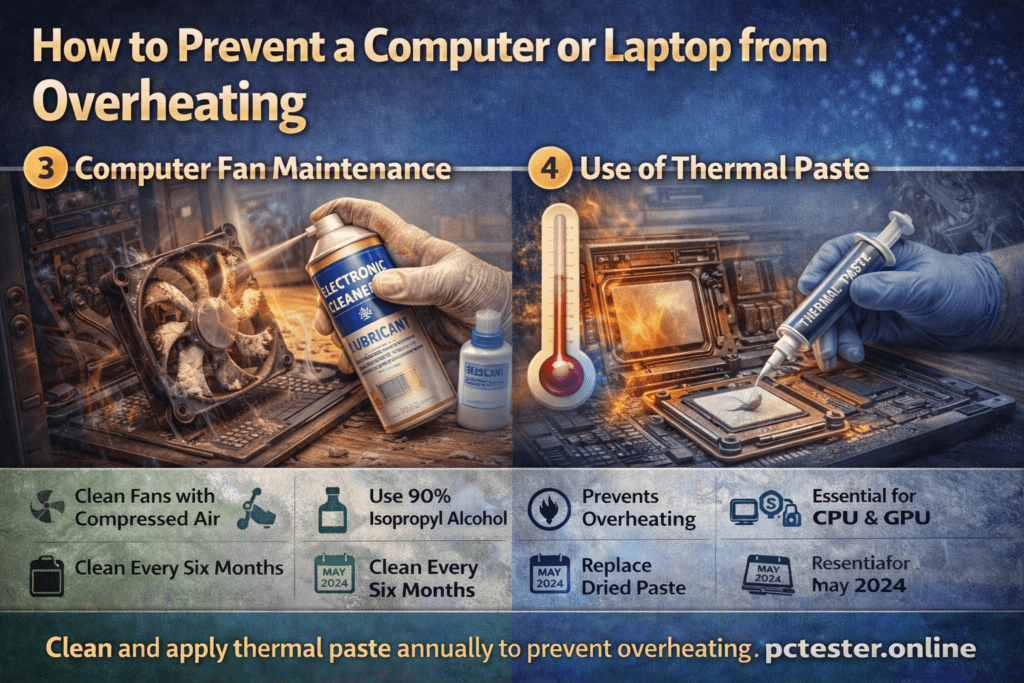
3. Computer Fan Maintenance
Clean your computer every six months to remove dust and dirt. Computer fans usually get dirty due to dust and air pollution. When this buildup becomes excessive, the fans may start to jam, causing their speed to slow down or stop working completely.
To prevent this, regular cleaning is essential. Remove the computer fans and clean them using an air compressor or compressed air. Carefully clean the fan blades and use 90% isopropyl alcohol to remove stubborn dirt and residue. This helps restore proper airflow and keeps the fan in good working condition.
4. Use of Thermal Paste
Thermal paste plays a crucial role in cooling the CPU and GPU by transferring heat to the heatsink, which is then cooled by the fan. If the thermal paste dries out, it can no longer perform this function effectively.
Thermal paste is extremely important, especially in gaming PCs. Without proper thermal paste, a computer can overheat and potentially fail. Make sure the thermal paste in your system is working properly and that your computer is not overheating.
If your computer is heating up and the thermal paste has dried out, replace it with fresh thermal paste. It is recommended to check at least once a year whether your computer needs new thermal paste to maintain optimal performance.
5. Keep Your PC Updated
A computer requires regular updates to function properly. Updates help fix issues related to both hardware and system performance. For this reason, always use an updated PC and keep the operating system up to date.
Make sure your antivirus and malware protection are active and regularly updated. Computer hardware is closely connected to software performance, and if your system is facing issues, it does not always mean the hardware is faulty—the problem may be software-related.
Always use updated and original software. Pirated software often contains viruses or malware that negatively affect system performance. As a result, the processor load increases, causing the computer to overheat.
6. Keep Your Hardware Up to Date
Try to avoid using very old computers. Ideally, use hardware that is only one or two generations behind the current technology. For example, older systems like Pentium 4 or Core 2 Duo were designed for the software of their time and are not suitable for modern applications.
As technology evolves, upgrading hardware becomes necessary. You should upgrade your computer based on your needs. If you are a regular laptop user, a newer-generation laptop without a dedicated graphics card may be sufficient. However, if you want to play modern games, you will need a computer with a compatible graphics card that can support your preferred games.

7. Close Unnecessary Programs
Close unnecessary applications and programs running in the background. Open the Task Manager and check which programs are using a high amount of CPU, then end those tasks.
Also, disable unnecessary startup programs so your computer does not experience heavy load when it turns on. Many computers freeze or lag for a short time after startup and then begin working normally. This usually happens because several programs automatically start when Windows boots, many of which are not actually needed.
8. Choose the Right Computer
Choosing the right computer can help you avoid many future problems. This means selecting a system that matches your actual needs.
For example, if someone is a gamer who plays demanding games but purchases a basic, everyday-use computer, they are likely to face overheating, lag, or performance issues later. This is because there is a significant difference between the specifications of a normal computer and a gaming computer.
Therefore, whenever you buy a computer, make sure it aligns with your usage requirements. Selecting the right hardware from the start ensures better performance, stability, and long-term reliability.

9. Research Before Buying a Computer
Before purchasing a computer, make sure to research the model thoroughly.
Many manufacturers release models that have built-in design flaws. Some computers are designed in a way that causes overheating issues from day one. Often, companies make laptops extremely thin to improve their appearance and attract customers. However, the thinner the laptop, the smaller the fans, and the less effective the cooling system becomes.
That’s why it is important to research a computer model carefully before buying it.
For example, Intel Core i7 11th and 12th generation processors consume a lot of power and generate heat very quickly. When these processors are paired with slim cooling fans, the fans fail to cool them properly, resulting in a condition known as thermal throttling.
Similarly, some laptop models suffer from poor airflow design. For example, certain HP Victus models and older Acer Nitro 5 models have airflow issues. In some older designs, both fans are positioned on the same side, which prevents heat from being expelled efficiently.
10. Choosing the Right Processor
Modern AMD Ryzen processors offer excellent performance and efficiency. However, older AMD processors—such as the FX series, A-series, and early APU series—were known for high power consumption and excessive heat generation. Because they overheated quickly, their performance often dropped.
When buying a laptop today, you will often hear about U-series and H-series processors.
U-series processors are designed for normal usage. They consume less power, generate less heat, and offer balanced performance.
H-series processors are high-performance processors and naturally run hotter.
If your laptop has an H-series processor, some heat is considered normal. However, if the system is overheating excessively, it may require servicing or improved cooling.

How to Check Your Laptop’s Processor
If you want to find out which processor your laptop has, follow these steps:
Open Task Manager
Go to the Performance tab
Check the processor name (for example: Intel Core i7-10700H)
Next, search for your laptop model on Google along with the term “thermal review.” This will help you determine whether overheating is a design flaw of the model or a problem that developed over time.
11. Loose Heatsink
Sometimes, due to a laptop being dropped or receiving a strong shock, the copper heatsink mounted on the processor can shift slightly out of position. The same issue can also occur in desktop PCs.
When the heatsink becomes loose, it cannot absorb and transfer heat efficiently. As a result, heat builds up inside the system, causing overheating in both laptops and desktop computers.
Faulty or Duplicate Power Supply
Another possible cause of overheating in laptops or desktop computers is a faulty or non-genuine power supply. In laptops, this may be due to a low-quality or incompatible charger.
If the power supply fails to deliver stable voltage or the required wattage, or if it produces electrical fluctuations, the system components do not receive sufficient power. To maintain performance, the processor compensates by drawing more load, which increases heat generation.
As a result, the laptop or desktop computer may start overheating. Always use a genuine, high-quality power supply or charger that meets the manufacturer’s specifications.

Conclusion
This article has covered all the possible causes of overheating along with their solutions. Overheating can occur due to one or multiple reasons. For best results, focus on hardware cleaning, thermal paste condition, proper airflow, software management, and a suitable operating environment.
If you are comfortable opening your hardware, clean the fans and replace the thermal paste when needed. Otherwise, make sure to get your laptop or desktop professionally serviced at least once a year. Regularly delete unnecessary files to keep your computer or laptop fast and cool.
If you want to perform a complete hardware check of your laptop or desktop—including the keyboard, mouse, screen, speakers, and more—you can visit our website and run a full system test.
About the Author

Adeel Farooq
Pakistan“I am a dedicated Hardware Specialist and Tech Blogger who started my journey back in 2002 with a Pentium 4 and a passion for GTA Vice City. Over the years, I have transformed my childhood curiosity into professional expertise in PC maintenance and thermal management. As the founder/lead contributor at pctester.online, I am on a mission to simplify complex hardware issues like ‘Thermal Throttling’ and help gamers worldwide keep their systems cool and fast.”

1 thought on “Why is My PC Overheating? 12 Causes, Fixes & Thermal Paste Guide”